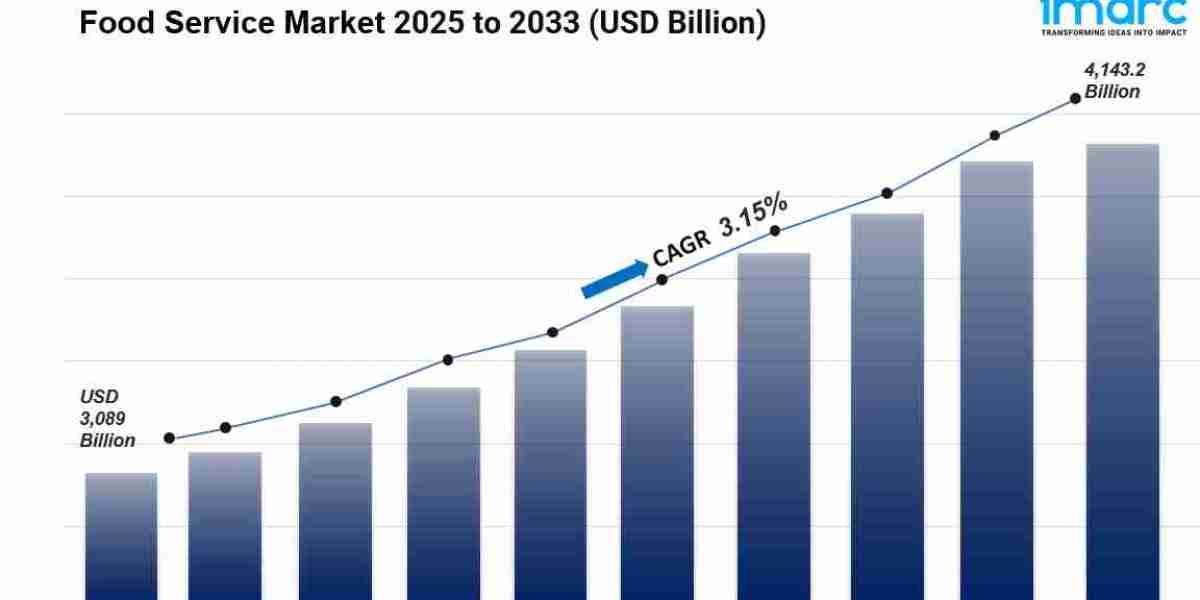
The global food service market size reached USD 3,089 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 4,143.2 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 3.15% during 2025-2033. Asia Pacific currently dominates the market, holding a significant market share in 2024. The market is experiencing stable growth driven by growing health-consciousness among individuals, rising number of online food delivery platforms offering enhanced convenience, increasing focus on health and wellness to maintain healthy and active lifestyles, and expanding preferences for culinary diversity and international cuisines.
Key Stats for Food Service Market:
- Food Service Market Value (2024): USD 3,089 Billion
- Food Service Market Value (2033): USD 4,143.2 Billion
- Food Service Market Forecast CAGR: 3.15%
- Leading Segment in Food Service Market in 2024: Full-Service Restaurants (by Types of Restaurants)
- Key Regions in Food Service Market: Asia Pacific, North America, Europe, Latin America, Middle East and Africa
- Top companies in Food Service Market: Chipotle Mexican Grill Inc., Costa Limited, Domino's Pizza, Inc., Jollibee Foods Corporation, KFC Corporation, McDonald's Corporation, Restaurant Brands International Inc., Starbucks Corporation, Subway IP LLC, Supermac's, Tim Hortons Inc, Wendy's International LLC, Yum! Brands, Inc, etc.
Request to Get the Sample Report: https://www.imarcgroup.com/food-service-market/requestsample
Why is the Food Service Market Growing?
The food service market is experiencing steady momentum as consumer lifestyles, preferences, and expectations evolve in fundamental ways. This isn't just about people eating out more—it's about how dining experiences are being redefined by technology, health consciousness, and changing social patterns that create new opportunities across the entire industry.
Health consciousness is reshaping what people order and where they choose to eat. Consumers are increasingly viewing food choices as integral to their overall wellness rather than just sustenance or indulgence. This shift is profound and accelerating. Restaurants and foodservice establishments are responding by offering menu items that cater to various dietary needs—vegetarian, vegan, gluten-free, keto, low-calorie, high-protein options. The days when healthy menu items were afterthoughts or limited to uninspiring salads are long gone. Now, health-focused offerings are menu highlights, carefully crafted to deliver nutrition without sacrificing flavor.
Foodservice providers are prioritizing fresh and locally sourced ingredients to meet demand for healthier and sustainable food options. Farm-to-table isn't just trendy restaurant marketing anymore—it's becoming standard expectation, particularly among younger consumers who care deeply about where their food comes from and how it's produced. This emphasis on ingredient quality and sourcing transparency builds trust while aligning with consumer values around health and environmental responsibility.
The reduction of unhealthy ingredients, offering of smaller portion sizes, and provision of detailed nutritional information help individuals make informed choices. Many restaurants now display calorie counts, allergen information, and ingredient lists prominently—not because regulations always require it, but because consumers demand it. This transparency empowers diners to align food choices with their health goals while building confidence in establishments that provide information openly.
Plant-based and vegetarian options are experiencing explosive growth worldwide. Many food service providers are introducing meatless alternatives and plant-based proteins to cater to the expanding vegan and vegetarian consumer base. Beyond dedicated vegetarian restaurants, mainstream establishments—including major fast-food chains—now feature plant-based burgers, chicken alternatives, and dairy-free options. This isn't niche anymore; it's mainstream menu diversification responding to real consumer demand.
Culinary diversity is driving excitement and exploration in dining. Increasing preferences for international cuisines are leading to incorporation of various flavors and fusion concepts on menus. Themed restaurants and pop-up food events showcase wide ranges of culinary traditions as consumers become more willing—even eager—to explore unfamiliar cuisines. The globalization of food culture through travel, media, and social platforms has created sophisticated, adventurous consumers who seek authentic experiences from different culinary traditions.
AI Impact on the Food Service Market:
Artificial intelligence is beginning to reshape food service in ways that address persistent industry challenges around labor efficiency, inventory management, customer experience, and operational consistency. While adoption varies widely—from cutting-edge implementations to barely started explorations—the trajectory is clear: AI will play increasingly central roles in how food service businesses operate.
Personalization represents one of AI's most visible applications. AI systems analyze customer data—order history, preferences, dietary restrictions, spending patterns—to provide personalized menu recommendations. Imagine opening a restaurant app and seeing suggestions tailored specifically to your tastes, dietary goals, and past favorites. Some systems can even adjust recommendations based on time of day, weather, or upcoming events. This hyper-personalization improves customer satisfaction while potentially increasing order values as recommendations surface items customers genuinely want but might not have discovered organically.
Dynamic pricing powered by AI allows restaurants to optimize pricing based on demand, time of day, ingredient costs, and competitive positioning. Similar to airline pricing strategies, some food service operations now use AI to adjust prices for delivery orders during peak times, offer strategic discounts during slow periods, or respond to competitor pricing changes in real-time. While dynamic pricing requires careful implementation to avoid customer backlash, when done transparently it can balance demand smoothing with revenue optimization.
Demand forecasting has been transformed by AI's ability to analyze historical sales data, weather patterns, local events, social media trends, and countless other factors to predict what menu items will be popular and when. This predictive capability dramatically improves inventory management—reducing food waste by ensuring appropriate ingredient quantities while avoiding stock-outs that disappoint customers and lose sales. For restaurants operating on thin margins where food costs represent major expenses, AI-driven forecasting delivers tangible bottom-line benefits.
Kitchen automation is advancing with AI-powered systems that can monitor cooking processes, adjust temperatures and timing based on real-time conditions, and even control robotic cooking equipment. While fully automated restaurants remain relatively rare, AI-assisted cooking equipment is becoming more common, particularly for standardized items like fries, burgers, or pizza. These systems ensure consistency—every item cooked to exact specifications—while freeing human staff to focus on complex preparations requiring judgment and creativity.
Chatbots and virtual assistants handle routine customer service inquiries, take orders, answer menu questions, and provide delivery updates without human intervention. Natural language processing allows these systems to understand casual conversation, regional dialects, and even handle complaints with appropriate empathy. For large restaurant chains handling thousands of daily interactions, AI-powered customer service dramatically reduces staffing requirements while providing instant responses that customers appreciate.
Segmental Analysis:
Analysis by Sector:
- Commercial
- Non-Commercial
Commercial sectors dominated the market in 2024, involving restaurants, cafes and coffee shops, fast food chains, food trucks, and fine dining establishments. Restaurants comprise wide ranges of dining establishments—fine dining restaurants, casual dining, fast-food chains, and quick-service restaurants (QSRs)—catering to diverse consumer needs for various dining experiences. From special occasion celebrations at upscale restaurants to quick lunches at fast-casual spots to convenience-focused stops at drive-thrus, commercial food service touches nearly everyone regularly.
Cafes and coffee shops offer relaxed environments for individuals to enjoy coffee, pastries, and light meals. These establishments have evolved beyond basic coffee service to become community gathering spaces, remote work locations, and social hubs. The coffee shop culture has become integral to urban lifestyles globally, with consumers viewing their regular coffee shop not just as transaction point but as extension of their lifestyle and identity.
Fast-food restaurants serve quick and convenient meals, often featuring standardized menus and fast service that appeal to time-constrained consumers. Despite ongoing health trends, fast food remains enormously popular due to unmatched convenience, affordability, and consistency. Major chains continue innovating with healthier options, premium offerings, and technology integration that keeps fast food relevant across demographic segments.
Non-commercial sectors include institutional food service, business and industry (B&I) food service, healthcare food service, education food service, and government and military food service. Institutional food service operates within schools, universities, hospitals, and correctional facilities, serving large volumes of meals meeting specific dietary and nutritional requirements. These operations face unique challenges—budget constraints, nutritional mandates, serving captive populations with varying needs—requiring different approaches than commercial operations.
B&I food service offers dining options within corporate and office settings, often including cafeterias, catering services, and vending machines. As workplaces evolve and companies compete for talent, quality food service has become important amenity rather than afterthought. Progressive companies view workplace dining as employee benefit supporting productivity, satisfaction, and culture.
Analysis by Systems:
- Conventional Foodservice System
- Centralized Foodservice System
- Ready Prepared Foodservice System
- Assembly-Serve Foodservice System
Conventional foodservice system, also known as traditional or cook-to-order system, dominated the market in 2024, involving preparing meals from raw ingredients in on-site kitchens. Food is prepared and cooked as customers place orders, offering high degrees of customization and freshness. Restaurants, fine dining establishments, and cafes generally use conventional systems to provide made-to-order dishes that can be customized to individual preferences and dietary requirements.
The conventional system's dominance reflects consumer preferences for fresh, customized food prepared specifically for them rather than mass-produced and reheated. Despite higher labor requirements and potentially longer wait times, the quality and customization advantages keep conventional systems popular, particularly in casual dining, ethnic restaurants, and upscale establishments where food quality is primary differentiator.
Centralized foodservice systems centralize food production in central kitchens where meals are prepared in bulk, then distributed to satellite locations for heating or finishing before serving. This includes large-scale catering operations, airline food production, and institutional settings like schools and hospitals. Centralized systems achieve economies of scale, ensure consistency across locations, and allow specialized facilities with optimal equipment and expertise.
Ready prepared foodservice systems involve meals partially cooked, portioned, then rapidly chilled or frozen for later use. Pre-prepared components are stored until needed, then reheated or finished in on-site kitchens or food service operations. Ready prepared service is common where quick service and efficiency are paramount—fast-casual restaurants, convenience stores, grab-and-go sections of supermarkets.
Assembly-serve foodservice systems use pre-packaged and portion-controlled meal components assembled or combined to create final meals with minimal cooking or preparation required. This includes fast-food outlets where ingredients like burger patties, buns, and toppings are assembled to make burgers, or salad bars allowing individuals to assemble salads from pre-cut ingredients. Assembly-serve systems prioritize speed and consistency while minimizing skill requirements.
Analysis by Types of Restaurants:
- Fast Food Restaurants
- Full-Service Restaurants
- Limited Service Restaurants
- Special Food Services Restaurants
Full-service restaurants dominated the market in 2024, also known as sit-down or table-service restaurants, offering comprehensive dining experiences where consumers are seated at tables and waitstaff takes orders, serves meals, and provides attentive service throughout dining experiences. These restaurants feature wide ranges of dishes including appetizers, main courses, desserts, and beverages. Full-service restaurants are known for enhanced ambiance and are popular choices for special occasions, corporate meetings, date nights, and leisurely dining experiences.
The segment's dominance reflects dining's social and experiential dimensions that extend beyond mere eating. Full-service restaurants provide occasions—celebrations, business discussions, romantic evenings, family gatherings—where food is important but the overall experience matters equally. This experiential element commands premium pricing and creates customer loyalty that transcends simple transaction relationships.
Fast food restaurants are characterized by quick service, limited menu options, and self-service or counter service models. These restaurants prioritize speed and convenience, often featuring standardized menus with familiar items. Customers place orders at counters, pay, and receive food quickly—often for takeaway or brief dine-in. Fast food chains are known for efficiency and affordability, making them popular choices for people seeking quick, convenient food solutions that fit busy schedules and limited budgets.
Limited service restaurants offer more streamlined and faster service than full-service restaurants while providing broader menu variety than fast food establishments. Customers may order at counters or through self-service kiosks, with food brought to tables. Limited service restaurants include fast-casual chains and cafes offering balances between convenience and wider menu selections. This segment has grown rapidly as consumers seek middle ground between fast food efficiency and full-service quality.
Special food services restaurants cater to specific culinary preferences or dietary needs. They include specialty restaurants focusing on particular cuisines (Italian, Mexican, sushi), health-focused restaurants offering organic, vegan, or gluten-free options, and food trucks, pop-up restaurants, and catering services providing unique and specialized dining experiences. This diverse category grows as consumer tastes become more sophisticated and specialized.
Analysis by Region:
- Asia Pacific
- North America
- Europe
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Asia Pacific dominated the global food service market in 2024 due to rising demand for wide ranges of food products among massive populations. Growing preferences for dining out and exploring varieties of cuisines among individuals offer positive market outlooks. Rapid adoption of food delivery apps and use of automation in food preparation and delivery bolster market growth throughout the region.
The region's sheer population scale—over 4.5 billion people—creates enormous market opportunities. Rising middle classes with increasing disposable incomes are driving dining-out frequency and willingness to spend on quality food experiences. Urbanization concentrates populations in cities where dining out becomes integral to lifestyles. Traditional street food cultures are evolving alongside modern restaurant concepts, creating vibrant, diverse food service landscapes.
China, India, Japan, and Southeast Asian nations each contribute substantial market portions while displaying distinct characteristics. China's massive population and rapid economic development have created the world's largest food service market by some measures. India's young population and growing middle class drive rapid expansion. Japan's mature market shows sophistication in quality, presentation, and service standards. Southeast Asia's diverse cultures create rich culinary landscapes attracting both local consumers and international tourists.
North America represents another key market region, driven by increasing demand for online food ordering and delivery services providing enhanced convenience. Integration of digital solutions into the food service sector supports market growth. Wide varieties of restaurant formats—from full-service dining establishments to fast-food chains to innovative fast-casual concepts—propel regional growth. The mature market shows sophistication in operations, technology adoption, and customer expectations while continuing to evolve as consumer preferences shift.
Europe maintains strong market presence with rising preferences for drive-thru services, mobile ordering apps, and quick-service dining accommodating fast-paced lifestyles. Increasing demand for convenient food services among people supports growth. Rising focus on food safety regulations and hygiene standards impels market expansion. European markets show strong emphasis on quality, sustainability, and culinary heritage while embracing innovations that enhance convenience.
Latin America exhibits growing potential driven by increasing technology adoption in food service sectors—mobile ordering, delivery platforms enhancing convenience and accessibility. Rising focus on fresh, locally sourced, and seasonal ingredients among individuals seeking healthier and sustainable dining experiences contributes to growth. Increasing preferences for mobile app-based delivery services and digital payment options propel market expansion.
The Middle East and Africa show developing markets primarily driven by increasing numbers of hotels, resorts, and luxury restaurants. Technology integration including online food delivery platforms and mobile payments streamlines food service experiences and enhances convenience. Rising demand for high-quality dining experiences among individuals strengthens market growth, particularly in Gulf Cooperation Council countries where tourism and hospitality sectors drive substantial food service demand.
Request Customization: https://www.imarcgroup.com/request?type=report&id=1310&flag=E
What are the Drivers, Restraints, and Key Trends of the Food Service Market?
Market Drivers:
The food service market benefits from powerful, interconnected drivers creating sustained momentum. Changing lifestyles with busier schedules and dual-income households drive demand for convenient dining options. When cooking at home becomes difficult to fit into packed schedules, restaurants, takeout, and delivery fill essential roles. This lifestyle shift represents fundamental change rather than temporary trend.
Rising urbanization concentrates populations in cities where dining out culture is stronger, variety is greater, and convenience is paramount. Urban density supports diverse restaurant ecosystems where specialized concepts can find sufficient customer bases to thrive. This urbanization trend continues globally, particularly in developing economies, creating expanding markets for food service.
Growing disposable incomes, particularly in emerging markets, allow more people to afford regular restaurant visits. As incomes rise, dining out transitions from occasional luxury to regular convenience or even routine. This income growth creates expanding customer bases and supports premiumization as consumers trade up to higher-quality dining experiences.
Social media influence drives restaurant discovery, builds buzz around new concepts, and creates aspirational dining experiences that people want to share. Instagram-worthy presentations, TikTok-trending foods, and online reviews shape consumer choices profoundly. Restaurants that understand and leverage social media can build followings and drive traffic in ways impossible before digital age.
Tourism growth creates steady demand for food service in destinations worldwide. Tourists eat out by necessity and often view local cuisine as integral parts of travel experiences. As global tourism continues recovering and growing, food service benefits from this transient but consistent customer stream.
Market Restraints:
Despite strong growth drivers, the market faces significant constraints. Labor shortages challenge food service operations globally. Finding, training, and retaining quality staff—from kitchen workers to servers to managers—represents persistent struggle. Labor-intensive nature of food service combined with demanding work conditions, modest wages, and irregular hours makes recruitment difficult. This labor challenge constrains growth, increases costs, and can compromise service quality.
Rising food costs and price volatility create margin pressures. Food service operates on relatively thin margins where ingredient cost increases significantly impact profitability. Passing costs to consumers through higher menu prices risks demand destruction, creating difficult balancing acts for operators.
Regulatory compliance requirements around food safety, labor laws, licensing, and health codes create administrative burdens and costs, particularly for smaller independent operators. While necessary for consumer protection, these requirements create barriers to entry and ongoing compliance costs that challenge profitability.
Intense competition characterizes food service markets. Numerous established players, new entrants, diverse formats, and delivery platforms all compete for limited consumer spending. This competition limits pricing power, requires ongoing innovation, and creates winner-take-all dynamics in some segments.
Economic sensitivity means food service experiences demand fluctuations with economic cycles. During recessions, consumers cut back on dining out, trade down to less expensive options, or shift from full-service to quick-service formats. While food service recovers during expansions, this cyclicality creates challenges for long-term planning and investment.
Market Key Trends:
Several dynamic trends are reshaping the food service landscape. Ghost kitchens and virtual brands represent significant innovation—commercial kitchens producing food exclusively for delivery without traditional restaurant footprints. These delivery-only concepts reduce real estate costs, enable rapid testing of new concepts, and allow restaurants to operate multiple brands from single kitchens. This trend accelerated during pandemic lockdowns but continues evolving as permanent feature of food service landscape.
Sustainability initiatives are expanding beyond niche to mainstream. Restaurants are reducing food waste, sourcing sustainable ingredients, using eco-friendly packaging, and implementing energy-efficient equipment. Consumers increasingly prefer establishments demonstrating environmental responsibility, making sustainability competitive advantage rather than just cost center.
Menu simplification has emerged as strategy for improving kitchen efficiency and food quality. Rather than extensive menus that require numerous ingredients and complex prep procedures, streamlined menus focus on fewer items executed excellently. This simplification reduces inventory complexity, improves consistency, minimizes waste, and can actually improve customer satisfaction by avoiding decision paralysis.
Subscription models and loyalty programs are creating recurring revenue streams and deeper customer relationships. From coffee subscriptions to meal plan memberships to points-based loyalty programs, restaurants are building systems that encourage repeat visits and provide predictable revenue. These programs generate valuable customer data while creating switching costs that reduce customer churn.
Alcohol-free beverages and mocktails are gaining prominence as sober-curious movements grow. Restaurants are developing sophisticated non-alcoholic drink programs featuring house-made sodas, kombuchas, shrubs, and elaborate mocktails. This trend responds to health consciousness, changing social norms, and recognition that profitable beverage programs needn't depend solely on alcohol.
Experiential dining extends beyond food to encompass entertainment, education, and immersion. Interactive dining experiences, chef's tables, cooking classes, and themed events create memorable occasions commanding premium pricing. This experiential dimension differentiates restaurants in crowded markets and creates social media moments that drive organic marketing.
Leading Players of Food Service Market:
According to IMARC Group's latest analysis, prominent companies shaping the global food service landscape include:
- Chipotle Mexican Grill Inc.
- Costa Limited
- Domino's Pizza, Inc.
- Jollibee Foods Corporation
- KFC Corporation
- McDonald's Corporation
- Restaurant Brands International Inc.
- Starbucks Corporation
- Subway IP LLC
- Supermac's
- Tim Hortons Inc
- Wendy's International LLC
- Yum! Brands, Inc
These leading providers are updating and diversifying menus to cater to changing consumer tastes and dietary preferences. They're offering healthier options, accommodating dietary restrictions, and incorporating trending ingredients that resonate with target demographics. Companies invest in innovative food preparation methods including automation and kitchen technology to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and maintain consistent quality across locations.
Major players are adopting online ordering and delivery platforms, implementing digital payment solutions, and using data analytics to personalize marketing and improve customer experiences. They prioritize sustainability by reducing food waste, using eco-friendly packaging, and sourcing responsibly to attract environmentally conscious consumers. These combined efforts strengthen market positions and drive industry evolution toward more sustainable, technology-enabled, customer-centric operations.
Key Developments in Food Service Market:
- 2025: The National Restaurant Association forecasts the foodservice industry will reach USD 1.5 trillion in sales, demonstrating robust industry health despite economic uncertainties. This projection reflects sustained consumer demand across multiple restaurant formats and dining occasions. The forecast indicates consumers continue prioritizing restaurant experiences and viewing dining out as essential rather than purely discretionary spending.
- 2024: Food-away-from-home prices remained elevated even as food-at-home inflation decelerated dramatically. This pricing dynamic created challenges for restaurants trying to balance necessary price increases with customer sensitivity. The divergence between grocery and restaurant pricing influenced consumer decisions about whether to cook at home or dine out, with some consumers reducing restaurant frequency in response to higher menu prices.
- 2024: Technology adoption accelerated across food service operations, with AI and machine learning enabling hyper-personalized dining experiences. Restaurants increasingly implemented systems analyzing customer preferences, predicting demand patterns, optimizing operations, and enhancing service quality. Digital menu boards, mobile ordering, contactless payments, and automated kitchen equipment became more prevalent across full-service, limited-service, and quick-service formats.
- 2024: Sustainability initiatives expanded beyond environmental responsibility to encompass social and economic dimensions. Leading restaurant chains committed to comprehensive sustainability programs addressing food waste reduction, sustainable sourcing, energy efficiency, and community engagement. These initiatives respond to consumer expectations while delivering operational efficiencies and supporting long-term business viability.
- Ongoing: Labor recruitment remains critical industry challenge with renewed focus on word-of-mouth recruitment tactics reinforcing drawing power and opportunity of industry careers. Food service companies are improving compensation, offering career development paths, enhancing workplace cultures, and highlighting industry opportunities to attract workers in competitive labor markets. Success in recruitment and retention increasingly differentiates winning companies from struggling ones.
If you require any specific information that is not covered currently within the scope of the report, we will provide the same as a part of the customization.
Speak to An Analyst: https://www.imarcgroup.com/request?type=report&id=1310&flag=C
About Us:
IMARC Group is a global management consulting firm that helps the world's most ambitious changemakers to create a lasting impact. The company provides a comprehensive suite of market entry and expansion services.
IMARC offerings include thorough market assessment, feasibility studies, company incorporation assistance, factory setup support, regulatory approvals and licensing navigation, branding, marketing and sales strategies, competitive landscape and benchmarking analyses, pricing and cost research, and procurement research.
Contact US:
IMARC Group
134 N 4th St. Brooklyn, NY 11249, USA
Email: sales@imarcgroup.com
Tel No:(D) +91 120 433 0800
United States: +1-201971-6302