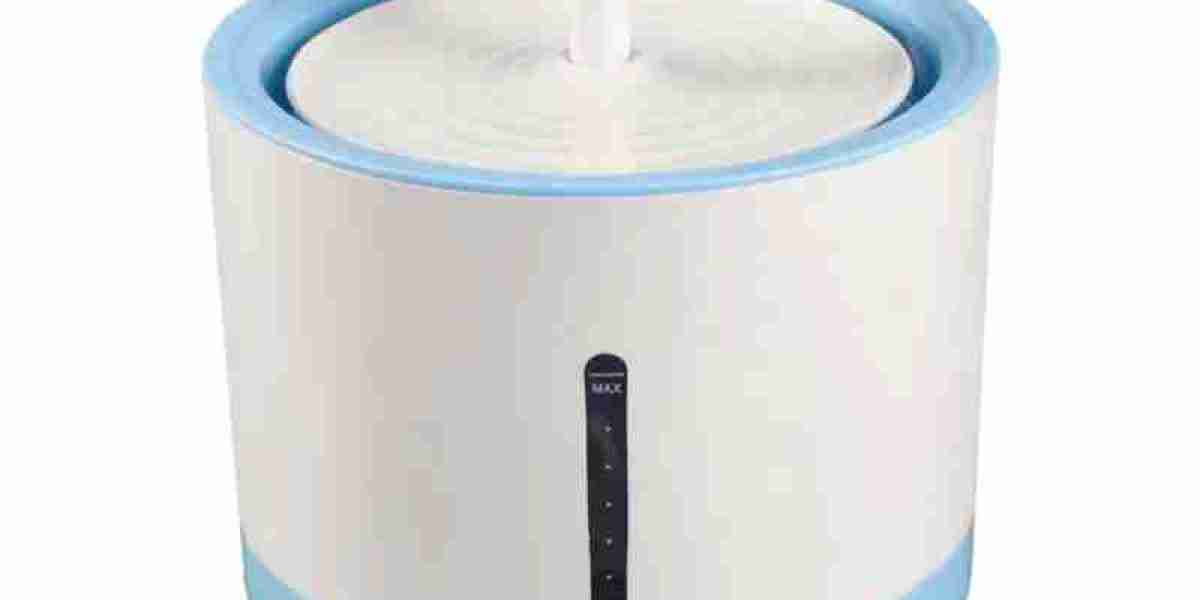
Kidney function relies heavily on consistent hydration to filter waste products and maintain internal balance. Many companion animals suffer from chronic dehydration simply because stagnant water bowls fail to encourage adequate drinking. Consulting a Pet Water Fountain Factory or researching circulation systems reveals how continuous fresh water access promotes healthier kidney function and prevents long term organ stress.
Kidneys require substantial water volume to perform filtration duties effectively. These organs process blood continuously, removing metabolic waste while preserving essential nutrients and minerals. Insufficient water intake forces kidneys to concentrate urine excessively, creating strain on delicate filtration structures. Over time, this concentrated processing environment increases risk of crystal formation and reduces overall filtration efficiency.
Stagnant water develops off putting tastes and odors that discourage drinking. Bacteria multiply rapidly in standing water, creating biofilm layers on bowl surfaces within hours. Animals possess keen senses that detect these quality changes, often choosing to drink less rather than consume unpleasant water. This instinctive avoidance protects against contamination but unfortunately leads to chronic mild dehydration affecting kidney performance.
Moving water naturally appeals to companion animals through both sound and visual stimulation. Flowing water remains cooler and fresher than stagnant supplies, qualities that attract animals seeking refreshment. The sound of trickling water triggers drinking instincts inherited from wild ancestors who sought flowing streams over still pools. This innate preference means circulation systems encourage more frequent drinking without requiring behavioral training.
Temperature stability matters for encouraging consumption. Room temperature stagnant water warms throughout the day, becoming less appealing especially during warmer months. Circulation keeps water moving through reservoir systems where it remains cooler and more refreshing. Animals demonstrate measurably increased consumption when water maintains pleasant temperatures compared to warm, sitting supplies.
Adequate hydration supports kidney blood flow essential for waste removal. Well hydrated kidneys receive sufficient circulation to flush toxins efficiently rather than allowing concentration buildup. This consistent flushing action reduces workload on individual nephrons, the microscopic filtering units within kidneys. Protecting these structures from excessive strain helps preserve kidney function throughout lifespan.
Older companions particularly benefit from encouraged hydration. Age related kidney changes reduce filtration capacity naturally, making adequate water intake increasingly critical. Senior animals often drink less due to reduced thirst sensation or mobility limitations. Appealing water sources positioned accessibly throughout living spaces support hydration needs during life stages when kidney health becomes vulnerable.
Crystal and stone formation decreases when urine remains properly diluted. Concentrated urine creates environments where minerals precipitate into solid formations that can obstruct urinary passages or irritate bladder linings. Maintaining dilute urine through consistent water intake prevents these painful conditions that frequently require medical intervention. Prevention through hydration proves far simpler than treating established urinary issues.
Multiple water access points accommodate animals spending time in various household areas. Single bowl locations may discourage drinking if companions must travel distances or navigate stairs when thirsty. Convenient access removes barriers to hydration, particularly important for animals with joint discomfort or those hesitant to leave comfortable resting spots.
Water quality affects both palatability and safety. Circulation systems incorporating filtration remove debris, hair, and particles that accumulate in standing bowls. Cleaner water tastes better and reduces ingestion of contaminants that kidneys must process. This dual benefit of improved taste and reduced impurity load supports both increased consumption and decreased organ stress.
Behavioral observation reveals individual hydration patterns. Some animals prefer drinking from flowing sources while others accept standing water readily. Recognizing preferences allows caregivers to provide appropriate options encouraging adequate intake. Flexibility in water delivery methods accommodates diverse drinking styles rather than forcing single solutions on all companions.
Understanding connections between water freshness, drinking behavior, and kidney health informs better hydration strategies. Supporting kidney function through encouraged water consumption prevents complications while promoting vitality. Implementing circulation systems transforms hydration from passive bowl filling into active health support. For fresh water solutions designed to encourage healthy drinking habits and support kidney function, visit https://www.tallfly.net/product/ to review options suited to various household configurations and companion preferences.