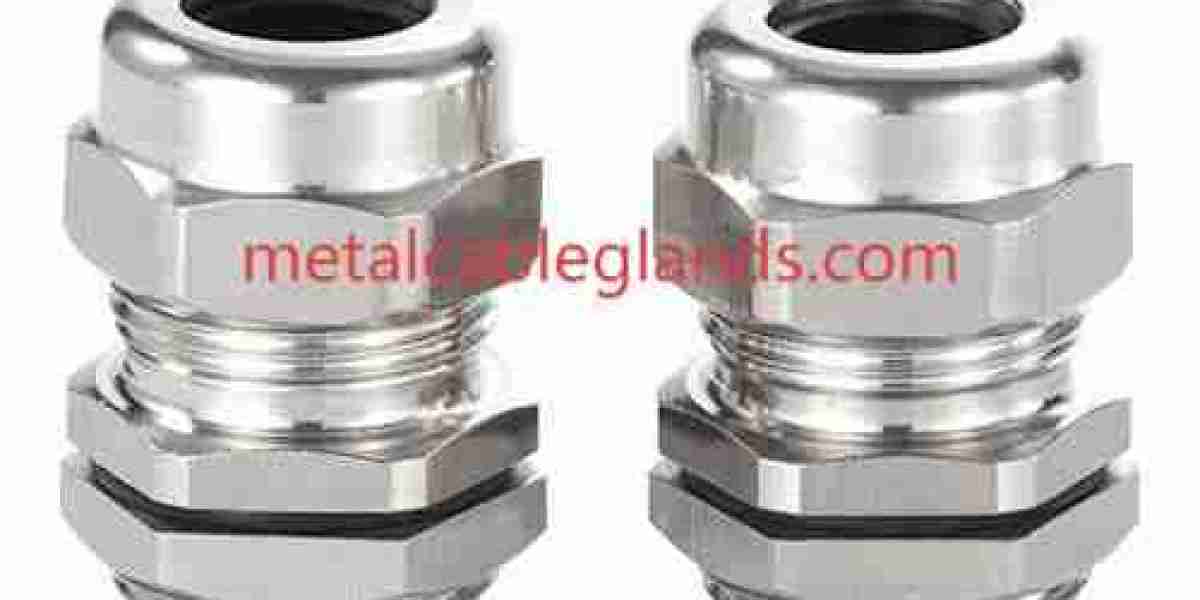
In modern electrical systems, the transition between different cable sizes is a common yet critical challenge, and the Cable Gland Reducer plays a quiet but essential role in ensuring that this transition is secure, reliable, and compliant across environments. Rather than being a simple accessory, it acts as a structural and protective bridge, allowing cable glands to maintain consistent sealing and mechanical stability when cable diameters vary. This adaptability makes it indispensable in installations where flexibility, durability, and long-term safety are expected as standard practice.
From a materials perspective, cable gland reducers are designed to withstand demanding operational conditions while maintaining compatibility with surrounding components. High-quality metallic options often emphasize corrosion resistance, surface stability, and structural strength, making them suitable for harsh industrial settings. Non-metallic variants, on the other hand, are valued for their lightweight nature, electrical insulation properties, and resistance to chemical exposure. Material selection is rarely arbitrary; it reflects the environment in which the reducer must perform, whether that involves exposure to moisture, vibration, or fluctuating temperatures.
Beyond material composition, the core function of a reducer lies in its ability to preserve the integrity of the entire cable entry system. When a cable gland is paired with a cable of a smaller diameter, gaps can compromise sealing effectiveness and strain relief. A well-designed reducer resolves this issue by creating a uniform interface that supports even pressure distribution and secure fastening. This ensures that external forces acting on the cable do not translate into internal stress on conductors or terminations, an outcome that is especially important in systems expected to operate continuously.
Performance characteristics extend further into long-term reliability. A reducer must maintain dimensional stability over time, resisting deformation that could lead to loosening or leakage. Surface precision contributes to smooth assembly and reduces the risk of cross-threading or uneven tightening during installation. In environments with constant movement or vibration, consistent performance helps protect sensitive electrical connections from gradual wear, supporting overall system longevity without requiring frequent maintenance interventions.
In practical application, cable gland reducers are widely used across industrial automation, power distribution, and infrastructure projects. Manufacturing facilities often rely on them to standardize enclosures while accommodating different cable types across machines and control panels. In energy-related installations, reducers support organized cable routing while helping maintain enclosure integrity against environmental exposure. Their role may be subtle, but without them, systems would require frequent redesigns or compromises in protection standards.
Transportation and logistics sectors also benefit from these components. Rail systems, ports, and large-scale facilities often involve retrofitting or upgrading existing electrical setups. Reducers allow engineers to integrate new cabling without replacing entire gland assemblies, saving time while preserving established safety practices. This adaptability aligns with modern engineering priorities, where efficiency and scalability are just as important as initial performance.
Within these varied applications, the importance of manufacturing expertise becomes evident. Companies such as Zhejiang Hongjuesi Connector focus on producing cable gland reducers that align with real-world installation needs, emphasizing material consistency, processing accuracy, and practical usability. Their approach reflects a broader industry shift toward components that support modular system design while maintaining dependable performance across different use cases.
As electrical networks continue to evolve, reducers are increasingly valued for their role in supporting flexible system architecture. Modern projects often involve mixed cable standards, imported equipment, and region-specific requirements. By providing a reliable interface between mismatched sizes, the Cable Gland Reducer enables smoother integration and reduces the risk of on-site improvisation that could otherwise compromise safety or compliance. This function supports cleaner layouts and more predictable installation outcomes.
In global markets, attention is also turning toward component standardization and supply chain reliability. Reducers that are designed with compatibility in mind help simplify procurement and inventory management. Installers and engineers can rely on familiar forms and functions, reducing learning curves and minimizing installation errors. This practical benefit further reinforces their value beyond purely mechanical considerations.
Toward the end of the installation chain, access to consistent product information and technical support becomes just as important as the component itself. Many professionals turn to established suppliers for insight into application scenarios, material options, and best practices. For those seeking additional reference and product context related to cable gland reducers and associated solutions, useful information can be found through Zhejiang Hongjuesi Connector’s product resources at https://www.metalcableglands.com/product .